When asking this question the typical answer you’re going to get is likely to be about bitcoins mysterious creator Satoshi Nakamoto, how there are only 21 million bitcoins that will ever be created, and how to buy bitcoin before the price goes to the moon.
But we’re not we’re here for the hype, I’m going to give it to you straight.
Yes, magic internet money can be a bit complex but it doesn’t need to be complicated.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a network of computers (or nodes) that each record the transfer of value over a shared public ledger.
Each computer in the Bitcoin network that runs the full bitcoin software is referred to as a full node maintains a copy of the ledger. This ledger is called the blockchain, and the value that is transferred on it—is denominated in bitcoin.
What is a bitcoin?
Bitcoin with a capital refers to the protocol and lowercase b refers to the digital unit that is the medium of exchange on the blockchain.
This network was first launched in 2009, by the pseudonyms creator Satoshi Nakamoto. It is the first cryptocurrency, and the first digital currency to successfully implement the ability to use public-key cryptography for sending and receiving (or locking and unlocking) transactions instead of its traditional use in encrypting and decrypting messages. Private keys stored in Bitcoin wallets authorize the transfer of bitcoin for transactions created on the blockchain.
To really understand Bitcoin we have to ask the question that cypherpunks were asking themselves before it was created. How do we create a way to transfer value securely over the insecure internet?
At the time this was a difficult problem to solve because there was no known way to get computers distributed all over the world, to come to an agreed-upon timestamp and order for transactions to be received. If you read the original Bitcoin white paper, you’ll see that bitcoin was never referred to as a blockchain but instead it was referred to as a decentralized timestamp server or timechain. Bitcoin miners and full nodes create a system capable of keeping time without a third party.
What is the Blockchain in simple terms?
The blockchain is a digital ledger that stores its history of transactions in blocks that are linked (and hashed) together to make a provably unbreakable chain.
Because all of this information is digital the concept of blocks and chains isn’t literal, transactions are grouped together in data structures called “blocks”, and “chained” together by a hash function. This is why people use the words “block” and “chain refer to the blockchain.
What is a block (Bitcoin block)?
A block is a group of transactions that have been confirmed at the same time.
Take a look at the raw data for a block in the blockchain:
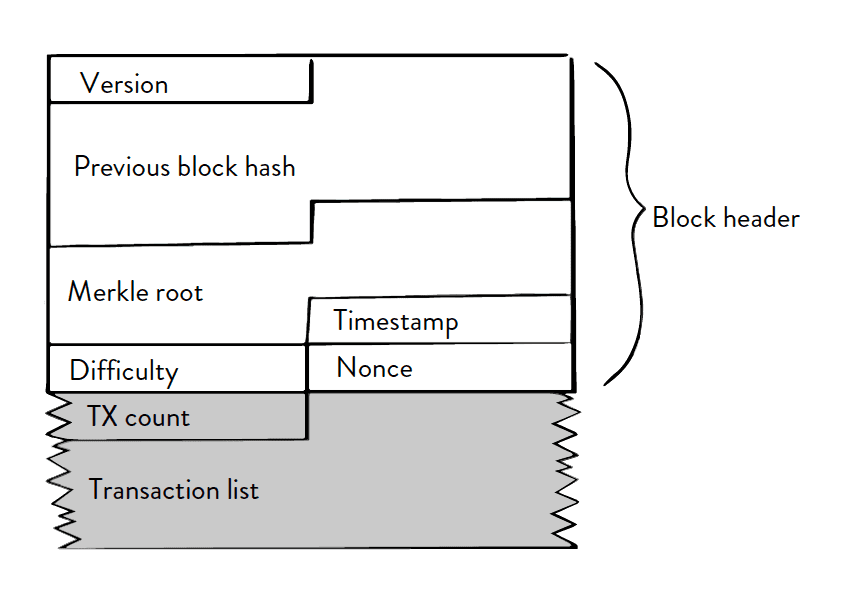
Blocks are where Bitcoin stores data. The bitcoin block structure is comprised of: a version, previous block hash, a Merkle root, timestamp, difficulty, nonce, transaction count, and most importantly the transaction list.
Every ledger needs to properly order transactions. If I’m paying you for a good or service we need a way of knowing when the money has moved from wallet to yours. We need to know when the funds are not mine anymore so that you can legally spend them.
But because this network is made up of computers all over the world network solving this problem this is a bit complicated. Even if transactions happened at “exactly the same time,” when two computers are in opposite parts of the world they are likely to disagree on the order of those transactions, because the news of each transaction travels at different speeds and arrives at different times.
The blockchain is made up of blocks that group transactions together. All transactions that are grouped in the same block, we say occurred at the same time. This gives the blockchain a final order for confirmed transactions.
What is a shared public ledger (Bitcoin ledger)?
The peer-to-peer network of Bitcoin users:
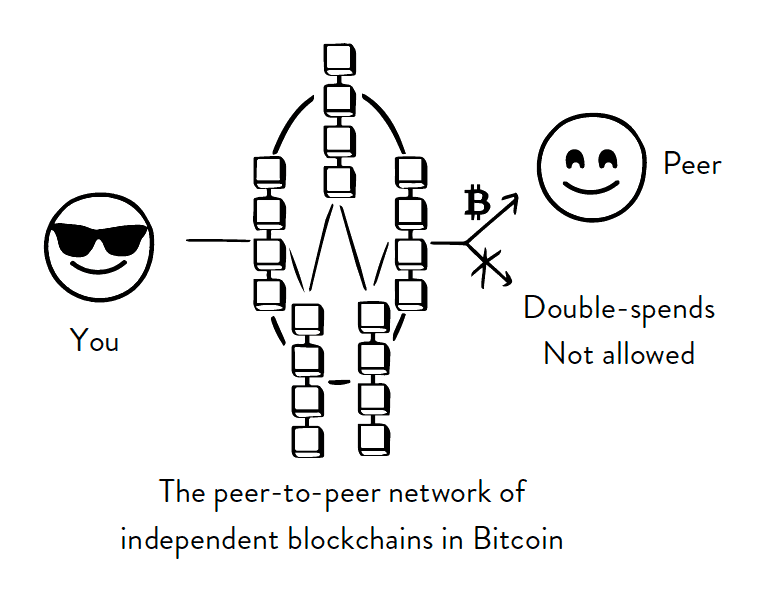
The public shared ledger is the record of all the bitcoin transactions on the blockchain. Because the ledger is stored by each of the independent full nodes in the network, we say that the ledger is “shared”. Instead of being shared, another way to think of it is that all of the ledgers are synchronized to the same state.
Every computer that runs the full bitcoin software (every “full node”) validates every transaction in the network to check that each is conforming to the same set of rules. The rules in Bitcoin are things like: users can’t spend funds they don’t have the private keys to, and miners can never be more than 21 million coins. Each cryptocurrency has its own ledger, with its own set of rules, so not all blockchains have the same properties.
Because Bitcoin is not centralized in any way, it’s not owned by a company or controlled by any organization. Payments that occur on this ledger can’t be stopped or censored. Bitcoin code is open-source, transactions on the network are public and permissionless, meaning that there is no asking an authority for permission, anyone who chooses to use it can. Transactions are processed trustlessly, without any middle-man or third party processor, which frees users from the need of banks.
The concept of having a single shared ledger for global transactions to take place was a massive innovation in cryptography and accounting. This ledger allows users to transfer value securely and peer-to-peer, and without censorship, which is not something that could be done with any previous payment system.
Is Bitcoin real money?
Money is defined as a medium of exchange, typically in the form of coins or paper, being issued by a government or bank. Because bitcoin isn’t bank or government-issued it’s more accurately defined as an asset, commodity, or currency, hence the term crypto “currency”. Bitcoin is a medium of exchange and a store of value, but many also people use it as a tool for speculation.
Government currency has one distinct advantage over Bitcoin: the government can create a demand for their currency, whereas the price of Bitcoin is put in the unsteady hands of the market. Any instability in the economy tends to mean that price of Bitcoin spikes up and down quickly as investors moving their funds into and out the asset looking for something that can hold their value. Few people really understand what Bitcoin is or what the blockchain is good for.